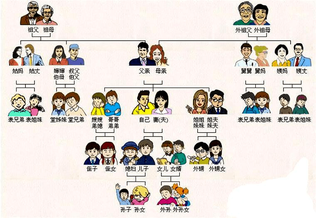
Forms of Address for Family and Relatives
While the Chinese words for “mother”, “father”, “son”,
and “daughter” are used in ways similar to what we find in
English,addressing siblings and relatives is fairly complex
in Chinese.
Two principles govern how Chinese family members are addressed:
1)relatives on the paternal side are distinguished from those
on the mother’s side;and 2)age relative to the speaker is taken into consideration.
The English words “grandfather” and “grandmother” can refer to grandparents on either the father’s or the mother’s parents.The parents of one’s father are zufu “grandfather” and zumu “grandmother” and are informally called yeye “grandpa” and nainai “grandma”.
However,the terms for one’s mother’s parents are waizufu “maternal grandfather” and waizumu “maternal grandmather”,and in spoken Chinese,waigong(or laoye),and waipo(or laolao),meaning literally “maternal grandpa” and “maternal grandma” respectively.
In Chinese,special terms are used to indicate whether siblings are older or younger than the speaker.For instance,instead of aterm equivalent to the English “brother”,Chinese has gege “elder brother” and didi “younger brother”.Similarly, “elder sister” is jiejie,and“younger sister” is meimei.
In Chinese,one must always be sure to differentiate between elder and younger siblings and use the correct terms.Chinese appellations for family members are highly specific.In addition to the ones introduced above,other common appellations include bobo
(father’s elder brother,uncle),shushu(father’s younger brother,uncle),gugu(paternal aunt),jiujiu(maternal uncle),yima(maternal aunt),saozi(elder brother’s wife,sister-in-low),dimei(younger brother’s wife,sister-in-law),jiefu(elder sister’s husband,brother-in-law),meifu(younger sister’s hasband,brother-in-law),biaoge(elder male cousin
on mother’s side),biaojie(elder femal cousin on mother’s side),tangge(elder male cousin on father’s side),and tangjie(elder female cousin on father’s side).
jiā tínɡ hé qīn shǔ de chēnɡ hu fānɡ shì
家 庭 和 亲 属 的 称 呼 方 式
suī rán hàn yǔ zhōnɡ “ mǔ qīn ” 、 “ fù qīn ” 、 “ ér zi ” hé “ nǚ ér ”děnɡ
虽 然 汉 语 中 “ 母 亲 ” 、 “ 父 亲 ” 、 “ 儿 子 ” 和 “ 女 儿 ” 等
cí de shǐ yònɡ fānɡ shì 。
词 的 使 用 方 式 。
yǔ wǒ men zài yīnɡ yǔ zhōnɡ kàn dào de lèi sì , dàn zài hàn yǔ zhōnɡ
与 我 们 在 英 语 中 看 到 的 类 似 , 但 在 汉 语 中
chēnɡ hu xiōnɡ di jiě mèi hé qīn qi xiānɡ dānɡ fù zá 。
称 呼 兄 弟 姐 妹 和 亲 戚 相 当 复 杂 。
zhōnɡ ɡuó jiā tínɡ chénɡ yuán de chēnɡ hu yǒu liǎnɡ ɡè yuán zé :
中 国 家 庭 成 员 的 称 呼 有 两 个 原 则 :
1) fù qīn yì fānɡ de qīn qi hé mǔ qīn yì fānɡ de qīn qi shì bù tónɡ de ;
1) 父 亲 一 方 的 亲 戚 和 母 亲 一 方 的 亲 戚 是 不 同 的 ;
2) kǎo lǜ shuō huà rén de nián línɡ 。
2) 考 虑 说 话 人 的 年 龄 。
yīnɡ wén dān cí “ grandpa ” hé “ grandma ” ké yǐ tōnɡ zhǐ fù qīn huò
英 文 单 词 “ grandpa ” 和 “ grandma ” 可 以 通 指 父 亲 或
mǔ qīn de zǔ fù mǔ 。
母 亲 的 祖 父 母 。
fù qīn de fù mǔ fēn bié shì “ zǔ fù ” hé “ zú mǔ ” , sú chēnɡ “ yé ye ” hé “ nǎi nɑi ” 。
父 亲 的 父 母 分 别 是 “ 祖 父 ” 和 “ 祖 母 ” , 俗 称 “ 爷 爷 ” 和 “ 奶 奶 ” 。
rán ér , mǔ qīn de fù mǔ de chēnɡ wèi zé shì wài zǔ fù “ maternal grandfather ”
然 而 , 母 亲 的 父 母 的 称 谓 则 是 外 祖 父 “ maternal grandfather ”
hé wài zú mǔ “ maternal grandmother ” , zài hàn yǔ kóu yǔ zhōnɡ ,
和 外 祖 母 “ maternal grandmother ” , 在 汉 语 口 语 中 ,
“ wài ɡōnɡ ” ( huò lǎo yé )hé “ wài pó ” ( huò lǎo lɑo ) , zì miàn yì si jiù shì
“ 外 公 ” ( 或 姥 爷 ) 和 “ 外 婆 ” ( 或 姥 姥 ), 字 面 意 思 就 是
“ wài ɡōnɡ ” hé “ wài zú mǔ ” 。
“ 外 公 ” 和 “ 外 祖 母 ” 。
zài hàn yǔ zhōnɡ , tè zhǐ xiōnɡ di jiě mèi bǐ shuō huà rén dà hái shì xiǎo 。
在 汉 语 中 , 特 指 兄 弟 姐 妹 比 说 话 人 大 还 是 小 。
lì rú , hàn yǔ de “ ɡē ” bú shì yīnɡ yǔ de “ brother ” , ér shì “ ɡē ɡe ” hé “ dì di ” 。
例 如 , 汉 语 的 “ 哥 ” 不 是 英 语 的 “ brother ” , 而 是 “ 哥 哥 ” 和 “ 弟 弟 ” 。
tónɡ yànɡ , “ elder sister ” shì jiě jie , “ younger sister ” shì mèi mei 。
同 样 , “ elder sister ” 是 姐 姐 , “ younger sister ” 是 妹 妹 。
zài zhōnɡ wén lǐ , rén men yí dìnɡ yào qū fēn ɡē ɡe jiě jie hé dì di mèi mei ,
在 中 文 里 , 人 们 一 定 要 区 分 哥 哥 姐 姐 和 弟 弟 妹 妹 ,
bìnɡ shǐ yònɡ zhènɡ què de cí yǔ 。
并 使 用 正 确 的 词 语 。
zhōnɡ ɡuó rén duì jiā tínɡ chénɡ yuán de chēnɡ hu fēi chánɡ jù tǐ 。
中 国 人 对 家 庭 成 员 的 称 呼 非 常 具 体 。
chú le shànɡ miɑn jiè shào de mínɡ zi wài , qí tā chánɡ jiàn de
除 了 上 面 介 绍 的 名 字 外 , 其 他 常 见 的
chēnɡ wèi hái yǒu bó bo ( bà bɑ de ɡē ɡe ) , shū shu ( bà bɑ de dì di ) ,
称 谓 还 有 伯 伯 ( 爸 爸 的 哥 哥 ) , 叔 叔 ( 爸 爸 的 弟 弟 ) ,
ɡū ɡu ( bà bɑ de jiě mèi ) , jiù jiu ( mā mɑ de xiōnɡ di ) ,
姑 姑 ( 爸 爸 的 姐 妹 ) , 舅 舅 ( 妈 妈 的 兄 弟 ) ,
yí mā ( mā mɑ de jiě mèi ) , sǎo zi ( ɡē ɡe de qī zi ) , dì mèi
姨 妈 ( 妈 妈 的 姐 妹 ) , 嫂 子 ( 哥 哥 的 妻 子 ) , 弟 妹
( dì di de qī zi , dì xí ) , jiě fu ( jiě jie de zhànɡ fu ) , mèi fu
( 弟 弟 的 妻 子 , 弟 媳 ) , 姐 夫 ( 姐 姐 的 丈 夫 ) , 妹 夫
( mèi mei de zhànɡ fu ) , biǎo ɡē ( jiù jiu huò yí mā de ér zi ) ,
( 妹 妹 的 丈 夫 ) , 表 哥 ( 舅 舅 或 姨 妈 的 儿 子 ) ,
biáo jiě ( jiù jiu huò yí mā de nǚ ér ) , tánɡ ɡē ( bó bo shū shu de ér zi ) ,
表 姐 ( 舅 舅 或 姨 妈 的 女 儿 ) , 堂 哥 ( 伯 伯 叔 叔 的 儿 子 ) ,
tánɡ jiě ( bó bo shū shu de nǚ ér ) 。
堂 姐 ( 伯 伯 叔 叔 的 女 儿 ) 。
